What Are Common Diabetes Treatments?
Diabetes is a chronic condition in which your body produces too little insulin or uses it inefficiently. Diabetes treatment is important to manage the symptoms of this disease, which is treatable but not curable. When diabetes is poorly controlled, the excess sugar in the bloodstream can cause serious health issues over time, including kidney disease, vision loss, and heart disease.
Diabetes treatment
There are three types of diabetes. Type 1 is believed to be the result of an autoimmune reaction that prevents the body from manufacturing insulin. This type is usually diagnosed at a young age. Type 1 diabetics must take daily doses of insulin for survival. With Type 2 diabetes, the body cannot use the insulin that it produces to keep blood sugar levels down. This type develops over many years and is generally diagnosed in adults. Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women. This type of diabetes places the baby at risk for health complications and increases the mother's risk of later developing Type 2 diabetes.
Depending on the type of diabetes, treatment will vary. However, a healthy lifestyle is a common factor in the management of all three types.
Physical activity
Exercise lowers blood sugar levels by transporting sugar to the cells, where it is consumed as energy. Exercise also raises the body's sensitivity to insulin, so less insulin is required to move sugar to the cells. A minimum of 30 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise for at least four days a week is recommended.
Healthy eating
While there is no specific diet for diabetes, the recommendation for diabetes treatment is to focus on foods low in calories and fats and high in fiber and nutrition, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. Daily food intake should limit refined carbohydrates, saturated fats, and sugary foods.
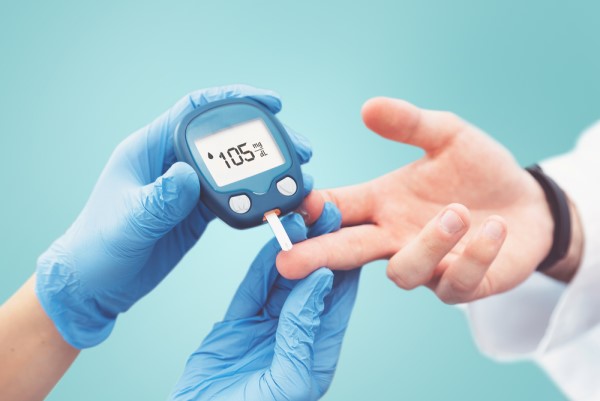
Sugar monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring as part of a diabetes treatment plan requires checking blood sugar levels to ensure they are within an established range. Type 2 diabetics who are not on insulin usually check their blood sugar levels using fingersticks up to three or four times a day, while Type 1 diabetics may use a continuous glucose monitor to check sugar levels on a much more frequent basis. In addition to daily monitoring, physicians recommend quarterly A1C testing to track the average blood glucose levels over the period of several months. An elevated A1C reading could indicate a need for changes to the existing diabetes treatment protocol.
Medications
Type 1 diabetics require insulin to survive. Some Type 2 diabetics and gestational diabetics also require insulin. Insulin is generally administered through an injection, pump, or artificial pancreas.
Oral or other injectable medications are also usually prescribed for Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetics. Some prescriptions stimulate the production of insulin. Other drugs for diabetes treatment inhibit the release of glucose from the liver. Additional medication options work through the stomach or intestine to impact the breakdown of carbohydrates. Another option is an SGLT2 inhibitor, which causes sugar to excrete through the urine instead of being reabsorbed into the blood.
FAQs
A diagnosis of diabetes can be scary, and patients often have a lot of questions. Here are some of the common questions that patients ask about this disease.
Will diabetes affect my life expectancy?
Unfortunately, having diabetes does cut short the lifespan of many people with this disease. It is one of the leading causes of death among both older and younger people. Diabetes alone is not usually the direct cause of death, but the comorbidities that go along with it, such as heart disease and kidney disease. However, the good news is that learning how to manage diabetes can increase your chances of living a longer and more healthy life.
Is diabetes genetic?
If you have recently been diagnosed with diabetes, you may wonder if your biological children are more prone to getting the disease. Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes have evidence of being passed through genetic factors. Make sure to talk to your children about the risk of developing this disease.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious and incurable condition that must be controlled to avoid life-threatening side effects. But this diagnosis does not have to be a death sentence. Diabetes treatment should include a combination of healthy habits and medications to allow individuals with the disease to live normal and active lives.
If you are at risk for diabetes or have been diagnosed with Type 1, Type 2, or gestational diabetes, contact our office to speak with a professional regarding a comprehensive diabetes treatment plan.
Check out what others are saying about our services on Yelp: Read our Yelp reviews.
Recent Posts
Walk-in clinic provide convenient, accessible health care for non-emergency medical needs, making it an ideal choice when immediate attention is necessary. Understanding when to visit a clinic can help patients save time, avoid unnecessary trips to the emergency room, and receive quality care for their health concerns. These clinics handle various issues, offering fast, professional…
Walk-in clinics provide minor illness treatment for patients seeking quick and effective healthcare to address their symptoms. These accessible facilities address non-emergency medical concerns without the need to wait days for the next available appointment. The following guide will review some of the most common minor illness treatments offered at walk-in clinics.Respiratory tract infections (RTIs)…
Ultrasounds are non-invasive diagnostic tools used in urgent care and primary care settings to assess various medical conditions. With these images, healthcare providers can identify and evaluate potential health concerns. Understanding when ultrasounds are necessary and what to expect during them can empower patients to make informed decisions about their care.An ultrasound diagnostic scan uses…
A pregnancy testing is one of the most effective ways to confirm pregnancy by detecting the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine or blood. In order to produce reliable results, it is important to understand the accuracy, timing, and different options of tests. While many people rely on over-the-counter pregnancy tests, it is important…


